Capturing dependency in timeseries using LSTM (temperature forecasting)
Project description:
Input: Data points which are comprised of 14 features such as air temperature, pressure, humidity, etc. Training set is comprised of 200000 data points while the validation set is comprised of 100000 data points and test set includes 120551 data points.
Goal: To predict the temperature for the next 24 hours.
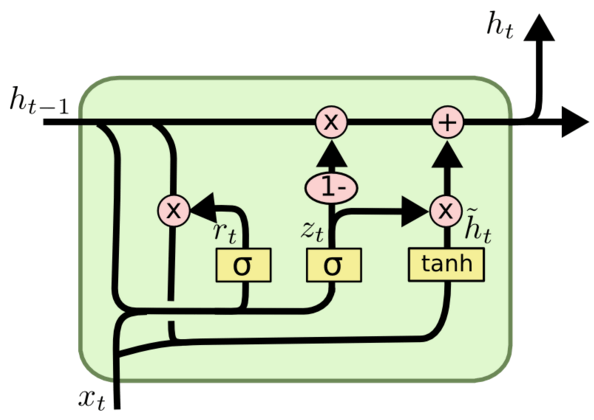
Network model: A sequence of 32 gated recurrent units (GRUs) is used to capture the dependency in timeseries data. One GRU is shown in the following figure:
The loss performance is shown in the following figure:
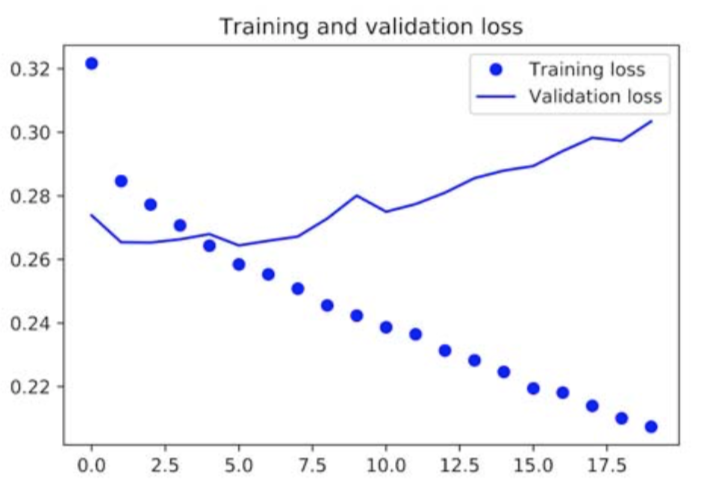
Modification:
To overcome the overfitting problem, regularization of the form dropout is used. For GRU, dropout reflects the rate of dropping the input units of the layer while recurrent_dropout shows the dropout rate of the recurrent units. The loss performance is shown in the following figure:
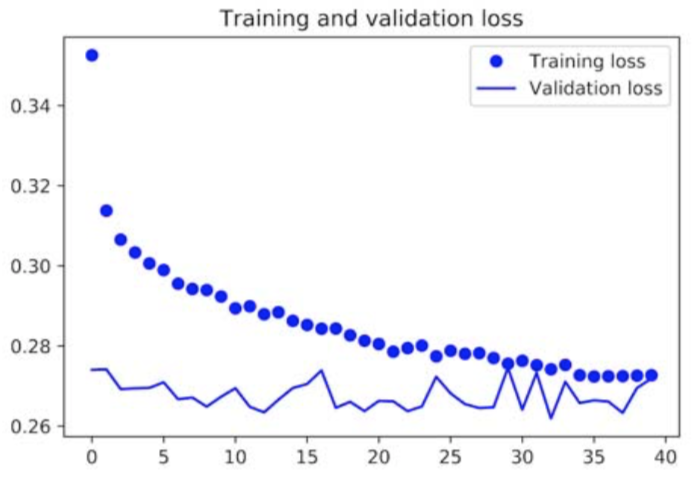
To see if the performance can be improved, one approach is to stack the GRU layers. One subtle difference is that, the output of first GRU layer now should be the entire sequence to be fed into the next GRU layer.
The loss performance is shown in the following figure:
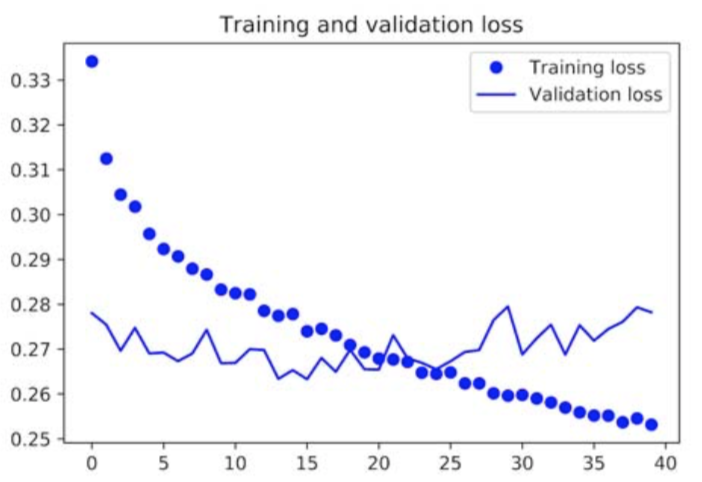
The last improvement is to use bidirectional GRU in which the dependency of data points in both forward and backward directions is analyzed.
The performance is the same as the first example and the reason is that the capacity of proposed model is used in the most efficient way.
The source code of this project is available in my Github page.
